India
People and Economy Book – 2
CHAPTER NO. 05
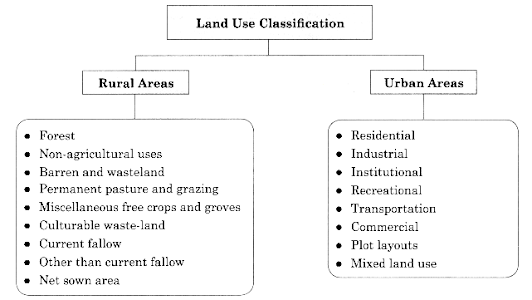
Land
Resources and Agriculture
Very
Short Answer type questions. (important Questions)
Q1. What do you mean by community forest?
Ans.
A
larger group than a house hold or family unit exercises rights of use and
carries responsibility of management is known as community forest.
Q2. What is the work of the Survey Dept. of India?
Ans. Measuring geographical area.
Q3. Define
the term Net Sown Area?
Ans. The physical
extent of land on which crops are sown & harvested is known as net sown
area.
Q4. What do you mean by the term fallow land?
Ans. Arable land
left uncultivated for one or more seasons to restore fertility of its soil.
Q5 How are pulses important for health?
Ans. Pulses are a
very important ingredient of vegetable food as these are rich sources of
proteins.
Q6. What is the reason of declining pastures and grassland in India?
Ans. Pressure from
agriculture land.
Q8. Name any two crops of wet farming.
Ans. Rice,
sugarcane.
Q9. Mention any two significance of pulses.
Ans. i. pulses are leguminous
crops which add fertility in the soil by concentration of nitrogen.
ii.
Pulses are the sources of protein for vegetarian people.
Q10. Which type of climate is required for coffee plantation in India?
Ans. Tropical
Region.
Q11. Classify the farming on the basis of moisture.
Ans. Wet land
farming and Dry land farming.
Q12. Write the names
of the two beverages crops?
Ans. Tea and coffee.
Q13. What is the
Percentage of Net sown area in India?
Ans. 54% of the total reporting area.
Q14. What is the
desire percentage of forest area in the country?
Ans. 33%.
Q15. Which body maintains the land use record?
Ans. Land, revenue department.
Q16. Full forms of these:
1. CPRs - Common property resources,
2. CI - Cropping intensity,
3. IAAP - Intensive agriculture area programme,
4. IADP - Intensive
agriculture district programme.
Q17. What is the ‘Aus’ ‘Aman and Boro’?
Ans. It is the type
of rice,(W.B) farmers grow three crops of rice called Aus, Aman, Boro.
0000
Q18. What is the Barani?
Ans. The farming
can be classified as irrigated and rainfall (barani).it is a type of farming.
Q19. What is the Narma?
Ans.
It
is a type of cotton. The long staple
(American) cotton called Narma.
Q20. What is the rank of India in the production of cotton?
Ans. 4thranks
of India in the world.
Q21. What is the red gram or pigeon pea?
Ans.
Tur is the second most important pulse crop
in the country .it is the also known as red gram or pigeon pea.
Q22. What is the name of three varieties of Coffee?
Ans. Arabica,
Robusta, Liberica.
Q23. What is the rank of India to produce sugarcane?
Ans.
2nd
ranks.
Q24. In which plantation India have first position?
Ans. Tea.
Q25. In which of the following group of countries of the world HYV of
wheat and rice were developed?
Ans. 1. Wheat –Mexico, 2. Rice – Philippines.
Q26. Define common property resource?
Ans. CPRs can be
defined as community’s natural resource, where every member has the right to
access and usage with specified obligations.2222
Q.27.How the total stock of agricultural land resource can be estimated?
Ans. An estimation
of the total stock of agricultural land resource [i.e., total cultivable land]
can be arrived at by adding up net sown area, all fallow lands and cultivable
wasteland.
Q28. Write down the formula for calculating the cropping intensity?
Or
How the crop intensity is calculated?
Ans. C.I in % age =
GCA\NSA X 100.
Q.29.What are the objectives of irrigation on which irrigated farming is
based?
Ans.1. Protective irrigation.
2. Productive irrigation.
Q30.What
is the further classification of rainfall farming?
Ans.1.Dry land farming.
2.
Wet land farming.
Q31.How food
grains are classified?
Ans. Food grain- 1.Cereals 2. Pulses.
Q32. How cereals are classified? Give examples.
Ans. Two type- 1. Cereals
– Fine grains – Rice, Wheat, Examples.
2.
Coarse grain
– Jowar, Bajra, Maize Examples.
Q33. Which
sector is effected land by increasing population?
Ans. Waste
agricultural land, Net sown area, Pastures area.
Q34. How
the rate of increase can be derived? Mention its formula?
Ans. Simple growth ie. [difference of values b/w the two points]
Value of terminal yr. – Base yr. / Base yr.
X 100.
Q35. Which is the second most important cereal crop in India?
Ans. Wheat.
Q36. Name
the crop which is food as well as fodder crop?
Ans.
Maize.
Q.37. In India, when did tea plantation started and where?
Ans.
In
1840s in Brahmaputra valley of Assam.
Q.38.What is the land human ratio in the country India as compared
to whole?
Ans.
Land
– human ratio is 0.31 hectare. And half of the world as whole.[0.59 hectare].
Q39. What is the twin menaces in Indian agriculture?
Ans. Droughts and
floods.
Q40. What is Green Revolution?
Ans. Boost out in
the production of food grain crops (1966-1967).
1.
Father of green revolution Norman Borelog in world.
2.
Father of green revolution M.S Swaminathan in India.
Benefited
crop by green revolution are Wheat, Rice. A benefited area is Punjab.
Q41. Describe Agricultural Problems in India?
Ans. 1. Erratic
Monsoon
2. Low Productivity
3.
Small Farm Size
4.
Lack of Land Reforms.
Q42. In which state consumption of fertilizers is most in India?
Ans. Punjab.
Q43. Which
departments maintained the records of land use?
Ans. Land revenue
department.
Q44. How
many types of tea leaves and what are their important features of these leaves?
Ans. Black tea leaves
which are fermented and green tea leaves which are unfermented.
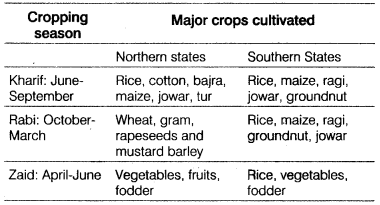
Q45. How many types of cropping seasons are there in India?
Ans. There are three main cropping seasons in India – Kharif, Rabi, and Zaid.
Q46. Define
Current Fallow?
Ans. This is the land
which is left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year.
Q47. Define
Fallow other than Current Fallow?
Ans. This is also a
cultivable land which is left cultivated for more than a year or less than five
years.
Q48. Define
Barren and Waste land?
Ans. The land which may
be classified as a waste land such as barren hilly, terrains, desert lands,
ravines, and etc.
Q49. Which
Department is responsible for measuring Geographical area?
Ans. The Survey of
India.
Q50. Give
some example of common property resource?
Ans. Community
forest, Pastures.
Q51. Distinguish
between Dry agriculture and wet agriculture:
Ans. 1.Dry agriculture: Practiced in
the area having less than 75 cm rainfall. Ex.- Ragi, Bajra.
2.
Wet agriculture:
Practiced in the area having more than 75cm of rainfall. Ex. -Rice.
Q52. Name
any factors which responsible for high productivity of crops in India?
Ans. 1. High Yielding
varieties of seed (HYV Seeds).
2. Fertilizers.
Q53. What
type of soils used for doing agriculture?
Ans. Good water
drain soil is known as Loam soil.
Q54. What
are the reasons in development of non- agricultural land?
Ans. Waste
agricultural land and non-agricultural land are take in used for secondary and
tertiary activities.
Q55. Where
the highest production of Cotton, Wheat, Sugarcane, Rice, Jute, Coffee, maize,
Mustard and Groundnut were found?
Ans. 1.Cotton: Gujarat,
2. Wheat: Uttar Pradesh,
3. Sugarcane: Uttar Pradesh,
4. Rice/Jute: West Bengal,
5. Tea: Assam,
6. Coffee: Karnataka,
7. Maize: Karnataka,
8. Groundnut: Gujarat,
9. Mustard: Rajasthan.
Q57.
Which trouble is called twin trouble in Indian agriculture?
Ans. Drought and
Flood.
Q58. Define Culturable Waste-land?
Ans. Any land which is left fallow for more than five years in this category.







1 Comments
Good post! This is a very good blog that I will definitely come back to many more times! Thanks for the article. Get best Hindi tuition online.
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.